Hydroforming technology has emerged as a revolutionary method in the manufacturing industry, providing solutions for creating lightweight, durable, and complex shapes using high-pressure hydraulic fluid. This innovative process has found applications across various industries, particularly in automotive, aerospace, and consumer products, offering numerous advantages over traditional forming methods like stamping and casting. In this article, we will explore the concept of Hydroforming technology, how it works, its benefits, applications, and the future of this cutting-edge technology.
What is Hydroforming Technology?
Hydroforming is a manufacturing process that uses high-pressure hydraulic fluid to shape malleable materials, typically metals such as aluminum, steel, or copper, into desired forms. This process is highly effective for creating parts that require high strength, precision, and lightweight structures. Hydroforming is most commonly used to form tubes and hollow parts, which can be found in industries like automotive, aerospace, and even in the production of consumer goods.
Unlike traditional manufacturing methods such as stamping, which involves shaping metal by pressing it between two dies, hydroforming uses hydraulic pressure to shape the material. The technique allows for the creation of more complex, intricate parts with fewer joints, reducing the overall weight of a product without compromising its strength or durability.
How Does Hydroforming Work?
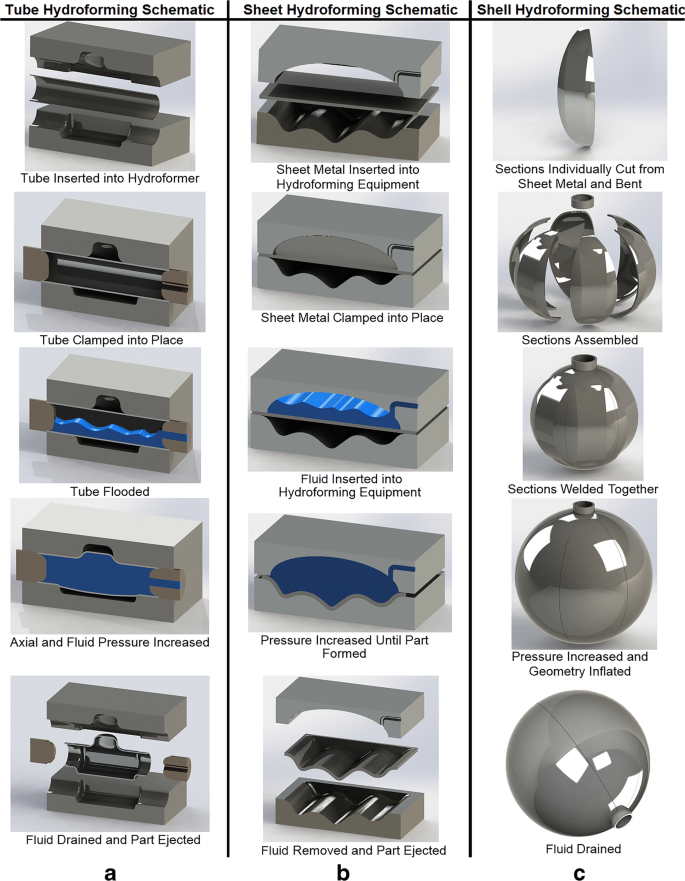
The hydroforming process involves several key stages that work together to achieve the desired shape. Let’s break down how the process works step by step:
1. Preparation of the Material
Hydroforming typically starts with a tube or sheet of material, such as steel or aluminum, that has been pre-cut to the desired length. The material is often annealed, or heated, to increase its malleability and make it easier to shape. The material is then placed inside a die or mold that will give it the desired shape.
2. Insertion of the Material into the Mold
Once the material is prepared, it is placed into a specially designed mold. This mold is typically made of two halves, one of which will be fixed while the other moves to apply the pressure. The material is inserted into the mold cavity, and the mold is closed around the piece.
3. Application of Hydraulic Pressure
At this stage, the high-pressure hydraulic fluid is introduced into the tube or sheet of material. The hydraulic fluid exerts pressure from within the tube, pushing the material outward and forcing it to conform to the shape of the mold. The pressure can range from 10,000 to 75,000 psi (pounds per square inch), depending on the material and the complexity of the part being formed.
As the pressure is applied, the material begins to expand and flow into all areas of the mold, creating the final shape. This process is extremely precise, allowing manufacturers to create complex geometries and tight tolerances in the finished part.
4. Cooling and Solidification
After the material has been fully formed, the pressure is released, and the part is allowed to cool and solidify. Depending on the material, the cooling process can take different amounts of time. Once the part has cooled sufficiently, it is removed from the mold and undergoes further finishing processes such as trimming, welding, or surface treatment.
5. Inspection and Quality Control
After the hydroforming process is complete, the part is thoroughly inspected to ensure it meets the required specifications. This can include visual inspections, dimensional checks, and tests for structural integrity. The process is highly precise, and quality control measures are crucial to ensure that each part performs as expected.
Benefits of Hydroforming Technology
Hydroforming offers a variety of benefits over traditional manufacturing techniques, making it an attractive option for many industries. Some of the key advantages include:
1. Reduced Weight of Components
One of the primary benefits of hydroforming is the ability to reduce the weight of components. By using hydraulic pressure to form lightweight materials like aluminum or high-strength steel, manufacturers can create parts that are both strong and lightweight. This is particularly important in industries like automotive and aerospace, where reducing weight leads to improved fuel efficiency, performance, and lower emissions.
2. Increased Strength and Durability
Despite reducing weight, parts made using hydroforming technology often exhibit increased strength and durability. The high-pressure forming process results in a more uniform distribution of material, leading to a part with enhanced strength in critical areas. The process also eliminates the need for welds or joints, which are often points of weakness in traditionally manufactured parts.
3. Complex and Intricate Shapes
Hydroforming allows for the creation of parts with complex and intricate shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods like stamping or casting. This is particularly advantageous in industries like automotive manufacturing, where parts need to be both lightweight and have complex geometries. Hydroforming can create parts with smooth, seamless shapes, reducing the need for additional assembly or welding.
4. Cost-Effective Production
While hydroforming equipment can be expensive, the overall cost of production is often lower than traditional methods, especially when producing large quantities of parts. This is because hydroforming reduces the number of required steps and eliminates the need for additional tooling or welding. In addition, the precision of the process reduces the likelihood of defects or rework, which further contributes to cost savings.
5. Environmental Benefits
Hydroforming is an environmentally friendly manufacturing process. By reducing the amount of material waste and energy consumption, it contributes to sustainability. Additionally, the lightweight nature of hydroformed parts leads to reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
Applications of Hydroforming Technology
Hydroforming technology has found widespread use in various industries due to its ability to create lightweight, durable, and complex parts. Below are some of the key applications of hydroforming:
1. Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is one of the largest users of hydroforming technology. Hydroforming is particularly beneficial in the production of lightweight components like chassis parts, suspension components, and engine cradles. By using hydroformed parts, automakers can reduce the weight of their vehicles, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions without sacrificing strength or safety. The process is also used to manufacture intricate parts with complex shapes, such as exhaust manifolds and frame components.
2. Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry also benefits from hydroforming, particularly in the production of lightweight, high-strength components. Aircraft manufacturers use hydroforming to create parts like airframe components, wing structures, and brackets. The ability to create complex geometries with minimal weight is crucial in aerospace applications, where every ounce of weight saved can lead to significant improvements in performance and fuel efficiency.
3. Bicycle Manufacturing
Hydroforming has become a popular technique in the bicycle manufacturing industry, particularly for creating lightweight, strong, and aerodynamic frames. The process allows bicycle manufacturers to produce frames with unique, complex shapes that would be difficult to achieve using traditional manufacturing techniques. Hydroformed bike frames are often lighter and more durable than their welded counterparts, providing better performance for cyclists.
4. Consumer Goods and Industrial Products
Hydroforming is also used in the production of various consumer goods and industrial products, such as pipes, hydraulic components, and structural parts. Its ability to create durable and complex shapes makes it ideal for manufacturing products that require both strength and precision. Hydroforming is often used in industries where high-performance parts are necessary, such as the medical device or energy sectors.
Challenges and Limitations of Hydroforming
Despite its many benefits, hydroforming technology does come with some challenges. One of the key limitations is the high cost of the initial setup, including the specialized molds and equipment required for the process. Additionally, hydroforming is primarily suited for producing parts with hollow or tubular shapes, so it may not be ideal for all types of components. Some materials may also be difficult to form using hydroforming, depending on their properties.
The Future of Hydroforming Technology
As technology continues to advance, hydroforming is expected to become more widespread and efficient. Innovations in material science, hydraulic pressure systems, and computer-aided design (CAD) software will make hydroforming even more precise and cost-effective. As industries like automotive and aerospace continue to push for lighter, stronger, and more complex components, hydroforming technology will play a crucial role in meeting these demands.
Conclusion
Hydroforming technology is an innovative manufacturing process that has transformed industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. By using high-pressure hydraulic fluid to shape materials into lightweight, durable, and complex parts, hydroforming offers numerous advantages, including reduced weight, increased strength, and cost-effective production. As technology advances, hydroforming is set to become an even more integral part of modern manufacturing processes, helping industries produce high-performance parts while minimizing environmental impact.