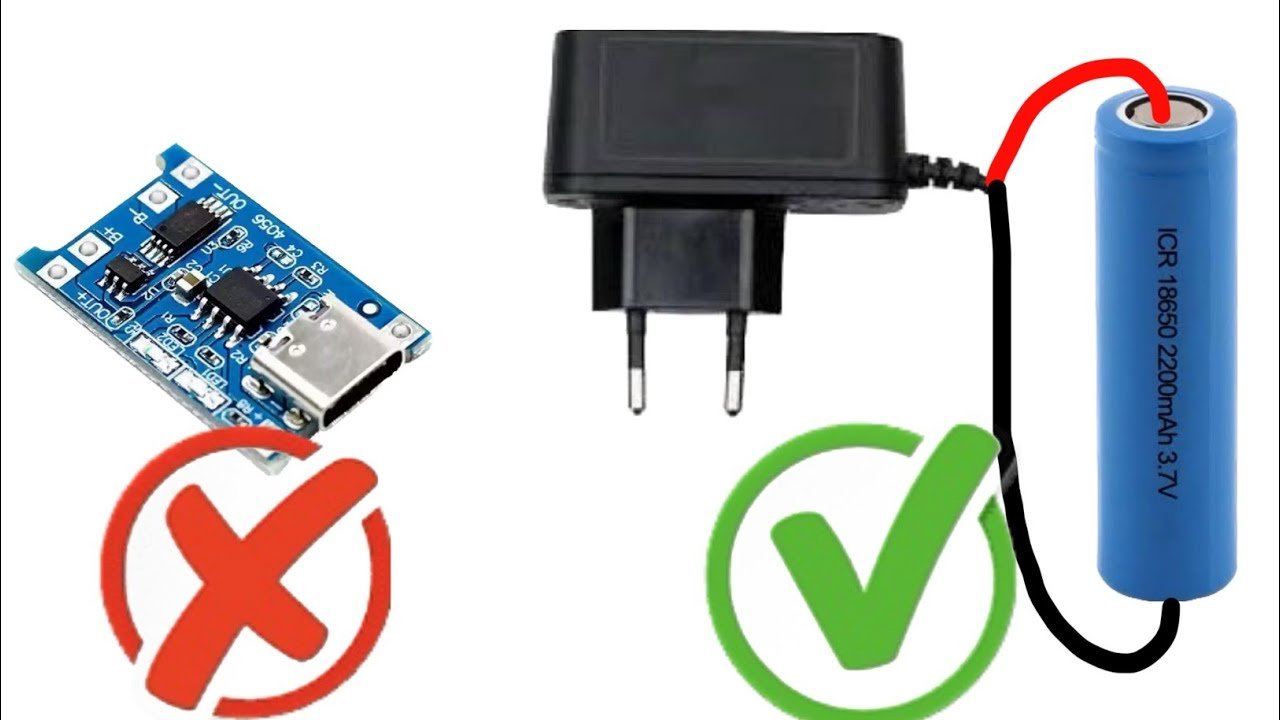
Lithium-ion batteries, or simply lithium cells, have become the power source of choice for everything from smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and solar energy systems. Their high energy density, lightweight design, and long cycle life make them ideal for many applications. However, proper charging of a lithium cell is crucial to ensure both safety and longevity. Incorrect charging methods can reduce the battery’s lifespan, pose safety risks, or even cause damage.
In this article, we’ll provide a detailed guide on how to charge a lithium cell correctly, covering key principles, safety tips, and the step-by-step process. Whether you’re using a lithium-ion cell in a DIY project, maintaining your electronic device, or working with high-capacity cells, understanding how to charge lithium batteries properly is essential.
Understanding Lithium Cells
Before we dive into the charging process, let’s briefly explore what a lithium cell is and why it requires specific care when charging.
- Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Batteries: These batteries are widely used in consumer electronics, electric vehicles (EVs), and other portable applications. They are rechargeable and consist of a positive electrode (cathode), a negative electrode (anode), and an electrolyte that allows the flow of lithium ions between the electrodes.
- Lithium-polymer (LiPo) Batteries: Another common type of lithium cell, similar to Li-ion but with a polymer electrolyte instead of liquid. LiPo batteries are often used in drones, RC vehicles, and portable electronics. They are also rechargeable but have some different charging characteristics than standard lithium-ion cells.
Lithium cells operate by the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode during charge and discharge cycles. Safe charging ensures that the cell’s voltage and current levels stay within specified limits, preventing issues such as overheating, overcharging, or short-circuiting.
Essential Steps to Safely Charge a Lithium Cell
Charging a lithium-ion or lithium-polymer cell requires careful attention to voltage, current, and temperature. Below is a step-by-step guide to ensure that you’re charging your lithium cell in the safest and most efficient manner.
1. Use the Correct Charger
The most important factor when charging a lithium cell is using a charger that is designed for that specific type of lithium cell. Unlike nickel-based batteries (NiMH or NiCd), lithium batteries require precise control over the charging process, including both voltage and current. A charger designed for lithium cells typically features the following:
- Constant Current (CC) Mode: This mode provides a steady current to the battery until it reaches its maximum voltage.
- Constant Voltage (CV) Mode: Once the battery reaches its maximum voltage, the charger switches to constant voltage mode, gradually reducing the charging current to prevent overcharging.
Using the wrong charger can result in overcharging, overheating, or even causing the battery to catch fire.
2. Check the Battery Voltage
Lithium-ion cells have specific voltage ranges, and charging them outside of this range can damage the cell or reduce its lifespan. For example:
- Nominal Voltage: For most lithium-ion cells, the nominal voltage is typically 3.6V or 3.7V.
- Fully Charged Voltage: A fully charged lithium-ion cell typically reaches 4.2V (although the exact voltage can vary slightly depending on the manufacturer).
- Discharge Cutoff Voltage: The lower cutoff voltage for most lithium-ion cells is 3.0V, but discharging the battery too much can damage it.
Before charging, always check that the battery voltage is within the acceptable range for the specific lithium cell you are using.
3. Connect the Battery to the Charger
Once you’ve confirmed that you are using the correct charger and that the battery is within its proper voltage range, you can connect the battery to the charger. Make sure to connect the positive terminal (anode) of the battery to the positive lead of the charger, and the negative terminal (cathode) to the negative lead.
- Polarity is Important: Reversing the polarity can cause short circuits or permanent damage to the battery. Always double-check connections.
4. Monitor the Charging Process
Lithium-ion batteries should not be left charging unattended for extended periods. Here are some key things to monitor during the charging process:
- Temperature: Lithium cells should not overheat during charging. The battery should feel cool or slightly warm to the touch. If it becomes hot, disconnect it from the charger immediately.
- Charging Current: Most chargers will display the charging current, which should gradually decrease once the battery reaches its full charge. This is normal behavior as the charger switches from constant current to constant voltage mode.
- Charging Time: The charging time will vary depending on the battery’s capacity and the charger’s output. For example, if you are charging a 2000mAh cell with a 1000mAh charger, it will take around 2 hours to fully charge.
5. Do Not Overcharge
While most modern chargers for lithium cells have built-in overcharge protection that automatically stops charging once the battery reaches its full voltage (typically 4.2V), it’s still a good idea to monitor the charging process. Overcharging a lithium battery can cause:
- Decreased Battery Life: Overcharging leads to capacity degradation and a shortened lifespan.
- Heat Generation: Excessive voltage can cause the battery to overheat, which may result in thermal runaway, a dangerous condition where the battery temperature rises uncontrollably.
Once the charging is complete, the charger should automatically stop. If you’re charging via a non-smart charger, you should manually disconnect the battery once it’s fully charged.
6. Avoid Charging in Extreme Temperatures
Lithium-ion cells should be charged at temperatures within a specified range. For most cells, this is typically between 0°C and 45°C (32°F to 113°F). Charging a lithium battery outside this temperature range can lead to:
- Overheating: Charging in high temperatures can cause the battery to overheat, resulting in reduced capacity, leakage, or in extreme cases, fire or explosion.
- Ineffective Charging: Charging in low temperatures can result in a failure to charge properly or even damage the cell.
To avoid these issues, ensure that you charge lithium cells in a well-ventilated environment that is within the temperature range recommended by the manufacturer.
7. Avoid Deep Discharging
Although lithium-ion batteries have a much lower self-discharge rate than older technologies, deep discharges (draining the battery completely) should still be avoided. Discharging a lithium cell to below 3.0V can cause capacity loss and even result in the cell becoming unresponsive.
Most chargers for lithium cells will stop charging when the voltage drops below a safe threshold. However, never discharge the battery completely unless it’s specifically designed to handle deep discharges.
8. Battery Storage and Maintenance
If you need to store your lithium cells for an extended period, it’s important to maintain their charge at a safe level. Most experts recommend storing lithium-ion batteries at about 40%-60% charge for optimal preservation. This prevents the battery from becoming over-discharged or overcharged during storage, both of which can damage the cell.
Safety Tips for Charging Lithium Cells
- Use Quality Chargers: Always use a charger that is specifically designed for lithium-ion or lithium-polymer cells. Cheap or generic chargers may lack overcharge protection or thermal management, which can lead to hazardous situations.
- Avoid Charging in Unattended Areas: Always charge lithium batteries in a safe environment where you can monitor their progress, especially if you’re charging high-capacity or large batteries.
- Do Not Charge Swollen Batteries: If a lithium battery becomes swollen or shows signs of damage (such as leakage, excessive heat, or an unusual odor), do not attempt to charge it. A swollen or damaged battery may be unsafe to charge and could pose a fire risk.
- Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for charging voltage, current, and temperature ranges. Different types of lithium cells may have different characteristics and requirements.
Conclusion
Charging a lithium cell may seem like a simple task, but it requires attention to detail and adherence to safety guidelines to ensure both the longevity of the battery and the safety of the user. By using the correct charger, monitoring the charging process, and avoiding extreme conditions, you can maximize the performance and lifespan of your lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries. Always prioritize safety and follow the best practices to enjoy reliable power for your devices and projects.